CCL NLSIU Launches the India Child Rights Index (ICRI)
What is ICRI?
The India Child Rights Index (ICRI) is a tool to understand the comparative status of children in all States and union territories of India in three domains: Nutrition and Health; Education and Protection. The Index is developed based on 60 indicators across these three domains. The index categorises groups of States based on their performance across these indicators, and also ranks them domain wise.
Why ICRI?
Multivariable indices help measure and identify the critical problems by breaking a major issue in a particular down to the micro level markers. Indices have been prepared and used by governments, policy makers and civil society to compare different contexts on the same themes. Developing a comprehensive index on child rights serves the purpose of drawing attention of the policy makers and other stakeholders towards the gravity of the situation and challenges in comparative terms, while reflecting on the root causes and overarching issues. Most importantly, ICRI is useful in identifying sector wise priorities for each of the States and identifying key data gaps pertaining to child rights.
Methodology
Comparable data for the indicators across three domains was drawn from latest official reports for all the States and union territories. Standardized scores were used to rank the States and composite scores were used to categorize them in five groups, from best to worst performers for each of them for each indicator. Read more about the methodology here.
Indicators
In addition to the ranking of States for each domain, a colour scheme has been used to visualize the data. The best performing States have been marked in green, whereas the poor performing States have been marked in red. The colour gradient from red to dark green reflects the poorest performing State to the best performing State, for a specific indicator. With respect to the child protection domain, the interpretation of the standardised scores is slightly different. States and Union territories may not be compared purely on the basis of crime figures. An increase in the crime numbers may be on account of certain citizen-centric initiatives undertaken by the police such as e-FIR filing mechanisms or women’s help desks. The increase or decrease in numbers, however, calls for professional investigation of underlying factors pertaining to local communities in order to address pertinent issues.
Click on the links provided below to view the respective indicators.
Nutrition and Health of children below five:
- Ranking of States (Child nutrition and health)
- Ranking of Union territories (Child Nutrition and Health)
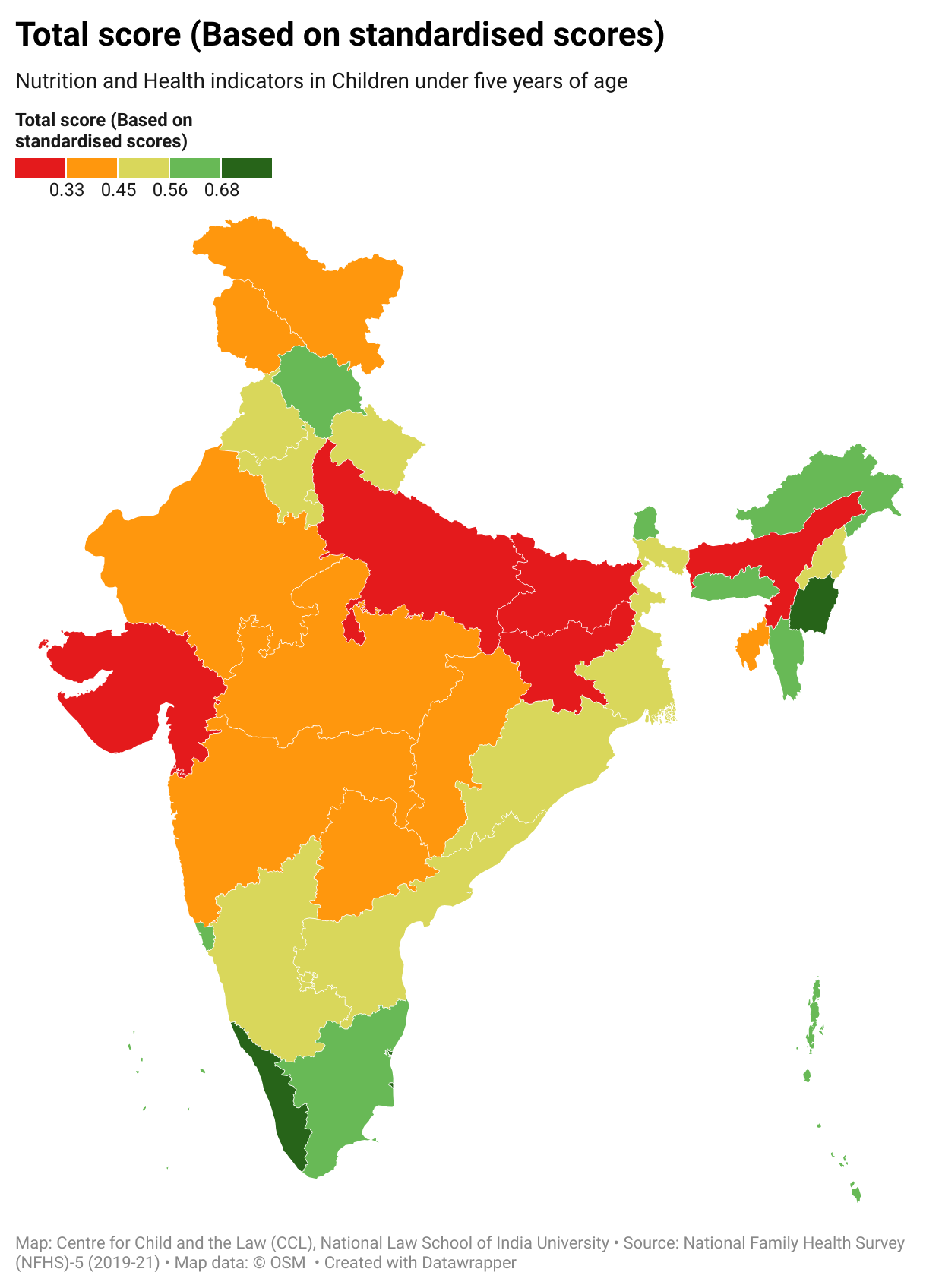
- Total scores
Undernutrition and Overnutrition in Children
Access to health services
Mortality rate
Infant Young Child Feeding Practices
- Breastfeeding within one hour
- Exclusive breastfeeding
- Children aged 6-8 months receiving solid or semi-solid food and breastmilk
- Breastfeeding children aged 6-23 months receiving adequate diet
- Non-breastfeeding children aged 6-23 months receiving adequate diet
- Total children aged 6-23 months receiving adequate diet
Women’s health
- Body Mass Index (women)
- Pregnant women aged 15-49 years who are anaemic
- All women aged 15-49 years who are anaemic
Education:
Adjusted Net Enrolment Ratio
- Adjusted net enrolment ratio – Upper Primary – Girls
- Adjusted net enrolment ratio – Upper Primary – Boys
- Adjusted net enrolment ratio – Primary – Girls
- Adjusted net enrolment ratio – Primary- Boys
- Adjusted net enrolment ratio – Secondary – Girls
- Adjusted net enrolment ratio – Secondary – Boys
Trained Teachers by Education Levels
- Percentage of trained teachers by levels of education (UDISE 2021-22) – Primary
- Percentage of trained teachers by levels of education (UDISE 2021-22) – Upper Primary
- Percentage of trained teachers by levels of education (UDISE 2021-22) – Secondary
- Percentage of trained teachers by levels of education (UDISE 2021-22) – Higher Secondary
Pupil-Teacher Ratio
- Pupil Teacher Ratio – Primary
- Pupil Teacher Ratio – Upper Primary
- Pupil Teacher Ratio – Secondary
- Pupil Teacher Ratio – Higher Secondary
Facilities across Govt. Schools
- Percentage of government schools with drinking water facility
- Percentage of government schools with functional toilets
- Percentage of government schools with library facility
- Percentage of government schools with computer facility
- Percentage of government schools with ramps for children with special needs
- Percentage of de facto population aged 2-4 years attending pre school (NFHS-5, 2019-2021)
- Learning outcomes
Child Protection:
Crimes under IPC
- Foeticide (Ss. 315 & 316 IPC)
- Exposure and abandonment (S. 317 IPC)
- Kidnapping and Abduction for the purpose of Begging ( IPC, Section 363 A)
- Kidnapping and Abduction of Minor Girls compelling them for marriage (S. 366 IPC)
- Procuration of Minor Girls (Sec.366 A IPC)
- Human Trafficking (Sec.370 & 370A IPC) (Children only)
- Rape (S. 376 IPC)
- Attempt to commit rape (S. 376 r/w S. 511 IPC)
POCSO
- Crimes under the POCSO
- Penetrative sexual assault and aggravated penetrative sexual assault (Ss. 4 & 6 of POCSO Act r/w S. 376 IPC) (BOYS)
- Penetrative sexual assault and aggravated penetrative sexual assault (Ss. 4 & 6 of POCSO Act r/w S. 376 IPC) (GIRLS)
- Penetrative sexual assault and aggravated penetrative sexual assault (Ss. 4 & 6 of POCSO Act r/w S. 376 IPC) (TOTAL)
- Sexual assault and aggravated sexual assault (Ss. 8 & 10 of POCSO Act r/w S. 354 IPC) (BOYS)
- Sexual assault and aggravated sexual assault (Ss. 8 & 10 of POCSO Act r/w S. 354 IPC) (GIRLS)
- Sexual assault and aggravated sexual assault (Ss. 8 & 10 of POCSO Act r/w S. 354 IPC) (TOTAL)
- Sexual harassment (S. 12 of POCSO Act r/w S. 509 IPC) (BOYS)
- Sexual harassment (S. 12 of POCSO Act r/w S. 509 IPC) (GIRLS)
- Sexual harassment (S. 12 of POCSO Act r/w S. 509 IPC) (TOTAL)
- Using child for pornographic purposes and storage of pornographic material involving child (Ss. 14 & 15 of POCSO Act) (BOYS)
- Using child for pornographic purposes and storage of pornographic material involving child (Ss. 14 & 15 of POCSO Act) (GIRLS)
- Using child for pornographic purposes and storage of pornographic material involving child (Ss. 14 & 15 of POCSO Act) (TOTAL)
JJ Act, Child Labour, Trafficking and other crimes
- Crimes under Juvenile Justice Act
- Crimes under Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act
- Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act 1956
- Cyber Crimes against children
- Other Special and Local Laws (SLL) Crimes Against Children
- Total Crimes Against Children (Indian Penal Code+Special and Local Laws)
Early marriages
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
- Urban Women aged 15-19 years who were already mothers or pregnant at the time of the survey
- Rural Women aged 15-19 years who were already mothers or pregnant at the time of the survey
- Women aged 15-19 years who were already mothers or pregnant at the time of the survey (TOTAL)
Institutions under JJ Act
- Number of Juvenile Justice Boards (JJBs)
- Number of Child Welfare Committees (CWCs)
- Number of Observation Homes (OHs)
- Number of Child Care Institutions (CCIs)
Read/download complete report